A new team will be taking over for out of hours oncall for Qlik Replicate and I tasked with training up a new team to diagnose and resolve problems with QR.
I thought it was a good idea to create some practice QR tasks in our development environment; intentionally put some problems in the tasks and let the new team diagnose the problem in a safe and no pressure scenarios.
I did the obvious ones; like put an incorrect password in an end point, put a typo in a filter criteria.
Looking for another scenario I thought – “Nothing better than a divide by zero error.”
Wait. That’s Illegal – Part 1
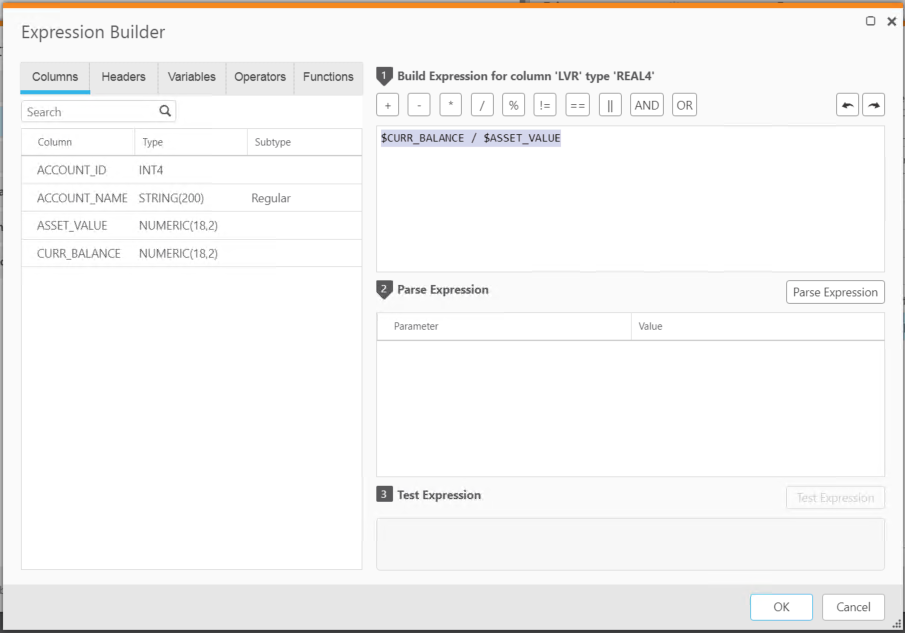
I created a simple table; with a field of CURR_BAL = 1000 and ASSET_VALUE = 0 and added a new field call LVR with the expression of:
$CURR_BALANCE / $ASSET_VALUE
Ran a full load expecting lots of nice and nasty error messages for the new team to investigate.
Hmm – no errors.
That’s not what I expected.
All the rows were transferred across and there was no errors or warnings in the log file, no data errors or anything.
I bumped up all the logging to “Trace” and reran the full load. Once again, no error messages.
Redirecting the output from the task to a kafka topic; I notice the records that had an intentional div/0 scenario was coming through as null.
{
"magic": "atMSG",
"type": "DT",
"headers": null,
"messageSchemaId": null,
"messageSchema": null,
"message": {
"data": {
"ACCOUNT_ID": 5,
"ACCOUNT_NAME": "Elissa",
"CURR_BALANCE": "10000.00",
"ASSET_VALUE": "0.00",
"LVR": null
},
"beforeData": null,
"headers": {
"operation": "REFRESH",
"changeSequence": "",
"timestamp": "",
"streamPosition": "",
"transactionId": "",
"changeMask": null,
"columnMask": null,
"transactionEventCounter": null,
"transactionLastEvent": null
}
}
}
Then I remembered – CDC expressions are built on sqlite syntax. Looking up how sqlite handles div/0 scenarios; by default sqlite will return a null instead of failing the query on a div/0.
Quoting from Sqlite – Difference Between engines
SQLite does not raise arithmetic exceptions (eg. divide by zero, 1/0). SQLite returns a NULL value for 1/0.
Wait. That’s Illegal – Part 2
I got past my div/0 conundrum after the explanation of what was happening and had a look at a “valid” record.
{
"magic": "atMSG",
"type": "DT",
"headers": null,
"messageSchemaId": null,
"messageSchema": null,
"message": {
"data": {
"ACCOUNT_ID": 1,
"ACCOUNT_NAME": "Alice",
"CURR_BALANCE": "12345.00",
"ASSET_VALUE": "500000.00",
"LVR": 0 <------------- Huh?
},
"beforeData": null,
"headers": {
"operation": "REFRESH",
"changeSequence": "",
"timestamp": "",
"streamPosition": "",
"transactionId": "",
"changeMask": null,
"columnMask": null,
"transactionEventCounter": null,
"transactionLastEvent": null
}
}
}
Again our LVR value was wrong.
12345.00 / 500000.00 should be 0.02469; instead of 0
A couple of things popped to mind.
It looked like the classic integer division issue that always catches out new (and experienced) programmer.
But that didn’t make any sense since the source fields were both numeric(18,2).
I checked the destination field that I added.
It was set to numeric(18,2), which isn’t precise enough for the LVR value but we still should have got 0.2 instead 0.
OK – QR must not like the “custom” precision of numeric(18,2) for the LVR field.
I tried forcing the LVR field data type to REAL(4).
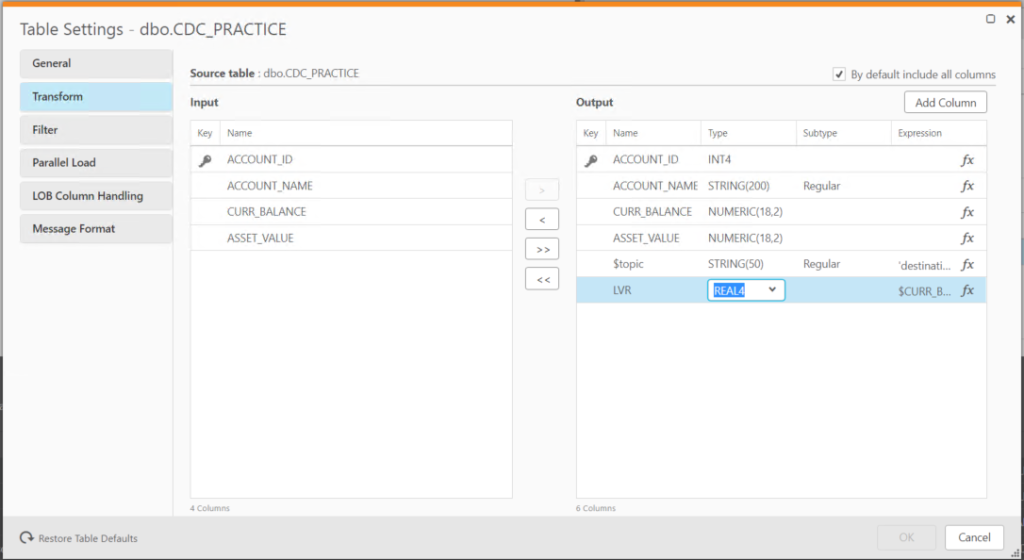
Still got the incorrect value for LVR
Maybe for some reason QR /sqlite treats the values coming in as an integer; even though the source data type is numeric(18,2) on the database.
Let’s give this a go:
CAST($CURR_BALANCE AS NUMERIC) / $ASSET_VALUE
^^ Nope
CAST($CURR_BALANCE AS NUMERIC) / CAST($ASSET_VALUE AS NUMERIC)
^^ Long shot but nope
CAST($CURR_BALANCE AS REAL) / $ASSET_VALUE
^^ At last success
{
"magic": "atMSG",
"type": "DT",
"headers": null,
"messageSchemaId": null,
"messageSchema": null,
"message": {
"data": {
"ACCOUNT_ID": 1,
"ACCOUNT_NAME": "Alice",
"CURR_BALANCE": "12345.00",
"ASSET_VALUE": "500000.00",
"LVR": "0.0246" <------------- Finally!
},
"beforeData": null,
"headers": {
"operation": "REFRESH",
"changeSequence": "",
"timestamp": "",
"streamPosition": "",
"transactionId": "",
"changeMask": null,
"columnMask": null,
"transactionEventCounter": null,
"transactionLastEvent": null
}
}
}
It works – but forcing a precise of numeric value to a floating point data type REAL leaves me uneasy; especially in a finance world were precision is needed.
I haven’t researched or tested whether this is a risk of generating an imprecise number through a division or not; something I will need to put on my todo list.
Conclusion
My design principle for Qlik Replicate tasks is to keep them as simple as possible.
Grab the data off the source and get it to the destination as quickly as possible.
By design principle I am against putting expressions in QR tasks:
- It is not as feature rich as other programming languages
- It hides business rules that adds a black box and complexity to the pipeline
Point 2 was the big one for me. I didn’t want downstream users messaging me every time there was an abnormality in the data. With no expressions in the QR tasks – I could rightfully say, “QR just grabs what it finds on the source database – go and talk to them”
Now with the discovery of these little “features” that could come from expressions; and more importantly no error or warnings about these “features”; it gives me even more incentive not to program in exceptions.
QR in my eyes is not an “ETL” tool – it is just a “EL” tool.
If your designers want complex expressions and transformations programmed into their data pipelines – it should be the downstream developers task.
That’s why they get paid the big bucks.